10 Best Organic Plant Fertilizers 2026 in the United States
Winner
FoxFarm Fertilizer Soil Trio Liquid Nutrient: Tiger Bloom, Grow Big, Big Bloom Bottles - (Pack of 3-1 Pint)
The FoxFarm Fertilizer Soil Trio Liquid Nutrient includes three different products: Grow Big, Big Bloom, and Tiger Bloom. Each serves a distinct purpose in promoting plant growth. Grow Big is a liquid concentrate fertilizer that supports lush vegetative growth. Big Bloom is an organic plant food suitable for use every time you water, and Tiger Bloom is a phosphorus fertilizer designed to enhance fruit, flower, and bud development. All three products are designed to work together, providing comprehensive support for vigorous growth and abundant yield.
Most important from
23976 reviews
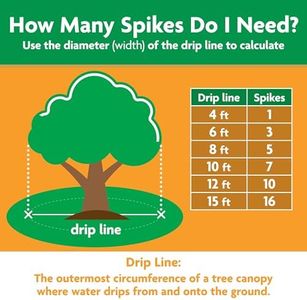
Miracle-Gro Fruit & Citrus Plant Food Spikes
Miracle-Gro Fruit & Citrus Plant Food Spikes are specifically designed for those looking to enhance the growth of their fruit, citrus, and palm trees. The spikes are easy to use, releasing nutrients directly into the root zone which promotes strong growth and lush foliage. This product is convenient because you only need to apply it once per season in both Spring and Fall, making it low-maintenance compared to other fertilizers that require more frequent applications.
Most important from
22496 reviews
Miracle-Gro Shake 'N Feed All Purpose Plant Food, For In-Ground and Container Plants, Feeds for up to 3 Months, 4.5 lbs.
Miracle-Gro Shake 'N Feed All Purpose Plant Food is a versatile option for both in-ground and container plants. One of its key strengths is the inclusion of vital micronutrients which aid in growing stronger and more vibrant plants. The product boasts a long-lasting feeding capability of up to 3 months, making it convenient for gardeners who prefer less frequent fertilizing.
Most important from
16878 reviews
Top 10 Best Organic Plant Fertilizers 2026 in the United States
Winner
FoxFarm Fertilizer Soil Trio Liquid Nutrient: Tiger Bloom, Grow Big, Big Bloom Bottles - (Pack of 3-1 Pint)
FoxFarm Fertilizer Soil Trio Liquid Nutrient: Tiger Bloom, Grow Big, Big Bloom Bottles - (Pack of 3-1 Pint)
Chosen by 1146 this week
Miracle-Gro Fruit & Citrus Plant Food Spikes
Miracle-Gro Fruit & Citrus Plant Food Spikes
Miracle-Gro Shake 'N Feed All Purpose Plant Food, For In-Ground and Container Plants, Feeds for up to 3 Months, 4.5 lbs.
Miracle-Gro Shake 'N Feed All Purpose Plant Food, For In-Ground and Container Plants, Feeds for up to 3 Months, 4.5 lbs.
Jobe’s Organics Granular Garden Fertilizer, Easy Plant Care Fertilizer for Vegetable Gardens and Tomato Plants, 4 lbs Bag
Jobe’s Organics Granular Garden Fertilizer, Easy Plant Care Fertilizer for Vegetable Gardens and Tomato Plants, 4 lbs Bag
Miracle-Gro Indoor Plant Food, Liquid Plant Food for Houseplants, Snake Plants, Peace Lilies, Flowers, Vegetables, Herbs and More, 8 oz., 2-Pack
Miracle-Gro Indoor Plant Food, Liquid Plant Food for Houseplants, Snake Plants, Peace Lilies, Flowers, Vegetables, Herbs and More, 8 oz., 2-Pack
Our technology thoroughly searches through the online shopping world, reviewing hundreds of sites. We then process and analyze this information, updating in real-time to bring you the latest top-rated products. This way, you always get the best and most current options available.